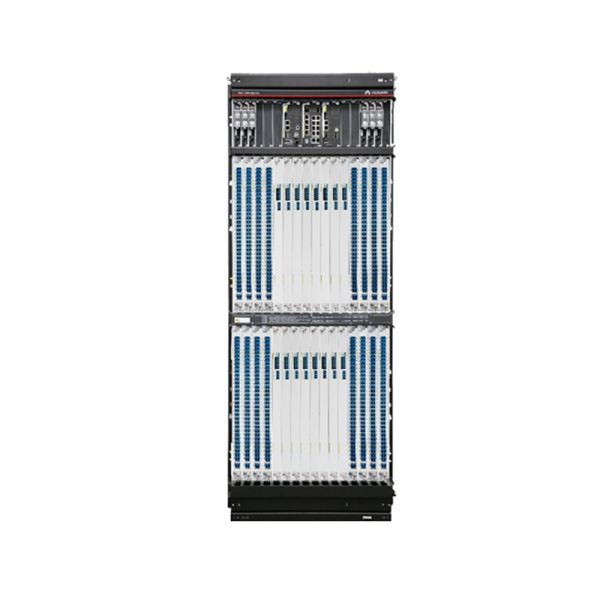
- Products
Expert Recommend
By Brands
By Categories
By Brands
By Brands
By Categories
By Brands
By Categories
By Brands
By Brands
By Brands
By Brands
By Brands
AR1200 Series Enterprise Routers
AR2200 Series Enterprise Routers
AR3200 Series Enterprise Routers
AR3600 Series Enterprise Routers
AR6000 Series Enterprise Routers
Huawei NetEngine Series Routers
Huawei Multi-Service Control Gateways
AR100 Series Enterprise Routers
AR120 Series Enterprise Routers
AR150 Series Enterprise Routers
AR160 Series Enterprise Routers
AR200 Series Enterprise Routers
Huawei AR550 Series Agile Gateways
Huawei AR502H Series Edge Computing IoT Gateways
Huawei AR502 Series Industrial Routers
Huawei AR509 Series IoT Gateways
Juniper CTP150 & CTP2000 Platforms
Juniper MX10003/MX10008/MX10016 Routers
Juniper MX2020 5G Universal Routing Platforms
Juniper MX960 5G Universal Routing Platforms
Juniper PTX1000/3000/5000/10000 Routers
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 1000 Switches
Cisco Catalyst IE3000 Rugged Switches
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 2000 Switches
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 4000 Switches
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 5000 Switches
Cisco Catalyst IE9300 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9311 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9316 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9317 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9318 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9319 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9320 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9321 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9322 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst IE9323 Rugged Series
Cisco Catalyst 1300 Series Switches
Cisco Catalyst 1200 Series Switches
NVIDIA Mellanox Quantum-2 CS8500 Modular Switch Series
Juniper EX4300 Series Ethernet Switches
Juniper EX2300 Series Ethernet Switches
Juniper EX4600 Series Ethernet Switches
Juniper EX3400 Series Ethernet Switches
Juniper EX3300 Series Ethernet Switches
Juniper QFX5200 Series Switches
Juniper QFX5100 Series Switches
Juniper QFX3000 Series Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 100 Series Entry Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 200 Series Mid-Range Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 400 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 600 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 1000 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 2000 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch 3000 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch T1000 Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch AX3660S Series Premium Switches
Fortinet FortiSwitch AX2340S Series Premium Switches
ExtremeSwitching X440-G2 Series
ExtremeSwitching X460-G2 Series
ExtremeSwitching X670-G2 Series
ExtremeSwitching VSP 7400 Series
Extreme Networks A-Series Switches
Extreme Networks S-Series Switches
Dell Networking X Series Switches
Dell Networking N1500 Switches
Dell Networking N3000 Switches
Dell Networking N4000 Switches
Dell Networking S4048-ON Switches
Dell Networking S4100-ON Switches
Dell Networking S3000-ON Switches
Dell Networking N1000 Switches
Dell Networking N2000 Switches
Dell EMC Networking PowerSwitch N2200 Series
Dell EMC Networking PowerSwitch N3200 Series
Cisco Firepower 1000 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 2100 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 4100 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 7000 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 8000 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 9300 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower Appliance Accessories
Cisco Firepower 3100 Series Appliances
Cisco Firepower 4200 Series Appliances
Huawei Next-Generation Firewalls
Huawei Application Security Gateways
Fortinet Network Security Platforms
Fortinet FortiWeb Web Application Firewalls
Fortinet FortiAnalyzer Centralized Solutions
Fortinet 360 Protection License
Fortinet Enterprise Protection License
Fortinet Dynamic Application Security Testing
Palo Alto PA-5000 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-5400 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-400 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-3200 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto Next-generation Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-5200 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-800 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-7000 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto PA-3000 Series Firewalls
Palo Alto Firewalls ION Devices
Cisco Catalyst 9100 WiFi 6 Access Point
Cisco Catalyst IW6300 Series Heavy Duty Access Points
Cisco 1560 Outdoor Access points
Cisco 1570 Outdoor Access Point
Cisco 1530 Outdoor Access point
FusionServer 1288H V5 Rack Server
FusionServer 1288H V6 Rack Server
FusionServer 2288H V5 Rack Server
FusionServer 2288H V6 Rack Server
FusionServer 2488H V5 Rack Server
FusionServer 2488H V6 Rack Server
FusionServer 5288H V5 Rack Server
FusionServer 5288H V6 Rack Server
Dell PowerVault MD1200 Storages
Dell PowerVault MD34XX Storages
Dell PowerVault MD38XX Storages
Hikvision Digital Video Recorders
Hikvision Network Video Recorders
Hikvision Intelligent Traffic Products
- Brands
- Service
ServiceProfessional ICT and IT product service guarantee, adding assistance to your project
Our Services
Support & Help
- Solutions
SolutionsExplore ICT solutions and select the right one for your demands, including Networking, Optical Network, and more.
Networking
Optical Network
Cloud
- News
- About Us
About UsHuaTenMax is an ICT and IT equipment wholesaler and supplier for Huawei, ZTE, Cisco, Fiberhome, Nokia, HPE, H3C, Lenovo, Potel, Ericsson, Juniper
Explore huatenmax.com
Contact Us
Events