Overview
5G is often called a breakthrough cellular network technology that makes everything in our lives easier, from robotic surgery to video calls to the advancement of artificial intelligence. However, apart from its faster speed, what is the uniqueness of 5G compared to previous iterations of cellular technology?
This article will introduce the concept and network architecture of 5G and explore the benefits and challenges of applying 5G in more areas. The article will also introduce how MPS solutions can help solve some challenges faced by 5G applications, such as power issues.

What is 5G?
5G is a global wireless communication standard released in 2019. It is the fifth generation of cellular network technology after 1G to 4G. In the 5G network architecture, the service area is divided into geographic units called "cells", each of which is centered on a base station. The base station handles the reception, processing, and transmission of signals between wireless devices (such as mobile phones) and the network.Communication between 5G wireless devices and cellular base stations (also called nodes) is achieved by sending or receiving radio waves through fixed antennas. These devices communicate via specific frequencies assigned by the nodes. For example, as you move around with your phone, it seamlessly switches communications between nodes to ensure continuous connectivity. If the signal weakens or is completely interrupted, it means that the phone is no longer in the coverage area of the node and there are no other available nodes nearby.
5G is the latest standard and is faster and more efficient than previous generations; in addition, it operates across three frequency bands (low-band, mid-band, and high-band), so it can provide consumers with wider signal coverage and faster speeds.
The main differences between the five generations of cellular network technology
| Generation | Average Data Rate (Mbps) | Application |
| 1G | 0.024 | Voice calls via wireless phones |
| 2G | 0.1 | Improved quality, text messaging |
| 3G | 2 | Email and video streaming, mobile data |
| 4G | 30 | Social media, HD streaming, apps |
| 5G | 60 to 1,000 | High-speed internet, AI networks, sensors |
5G Network Architecture
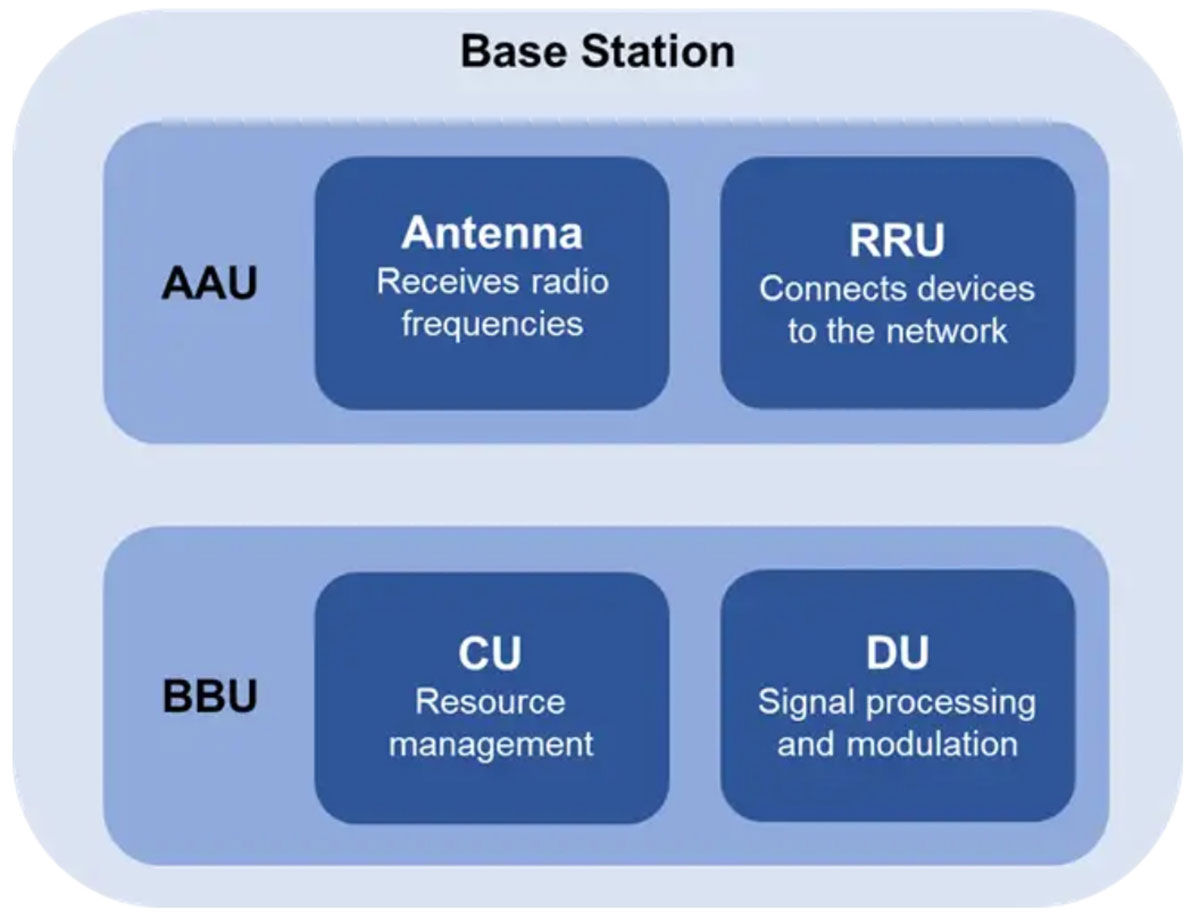
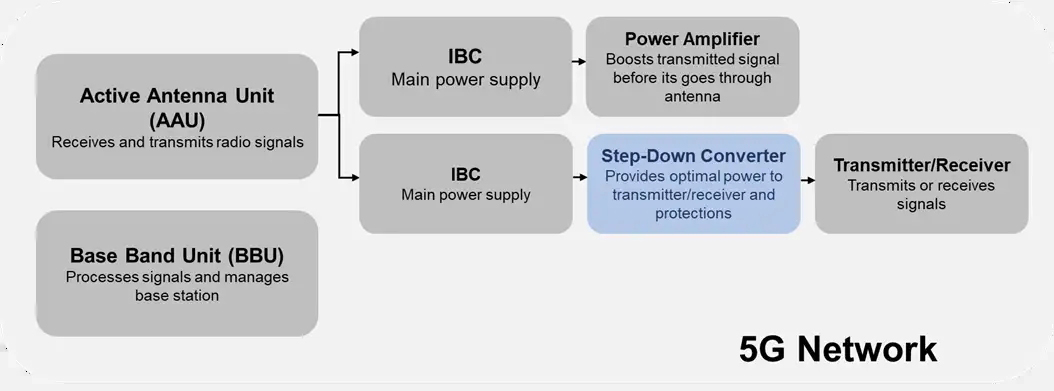
Base stations are the core components of 5G networks and consist of two major components: active antenna units (AAUs) and baseband processing units (BBUs).The AAU is responsible for receiving and sending radio signals, enabling communication between wireless devices and base stations. The AAU consists of two major components: an antenna that receives radio frequencies and a remote radio unit (RRU) that connects wireless devices to the wireless network.
The BBU is connected to the RRU and is responsible for controlling data traffic and performing data processing. The BBU is divided into centralized units (CUs) and distributed units (DUs). The CU provides advanced functions such as resource management, while the DU performs functions such as signal processing and modulation.
What benefits come with 5G network?
Compared with 4G, the biggest advantage of 5G is faster download and upload speeds, which allows users to communicate almost instantly. Faster download and upload speeds make it easier to connect online and join Internet discussions, send texts and pictures.
In addition, 5G has lower latency, which reduces the time it takes for data to be transferred between devices. This means that when you video call with friends, the video will not often freeze, and you can always see their real-time responses. Enhanced mobile broadband also allows people to watch higher-definition videos and interact with virtual reality.
Moreover, 5G is more suitable for densely populated areas because it supports simultaneous connections, which is crucial for smart homes that continue to add more Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as video doorbells, electronic smart locks, and smart thermostats controlled by mobile phones.
5G is not only beneficial to consumers, but also invaluable to certain markets. It promotes the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and is fast enough for chatbots such as ChatGPT to quickly organize people's questions and provide coherent answers. The medical field can also use 5G to achieve telemedicine and provide a reliable communication network between the accident site and the operator who needs to dispatch rescue services.
It is estimated that the industries that 5G can serve will continue to expand and provide people with new technologies that are faster, more reliable and higher quality.
Challenges of 5G
One of the biggest issues facing 5G is its low energy efficiency. 5G infrastructure requires a dense network of cells and base stations, which can be expensive and require long development times due to the coordination between construction teams and regulators. Although 5G is designed to be more energy-efficient than previous generations, it still has a more complex architecture and more sites. This leads to higher overall energy consumption, high costs, and may ultimately cause more environmental problems than it solves.5G systems require high power to support ultra-fast data transmission standards, which requires a trade-off between environmental friendliness and high speed. To ensure that 5G does not harm the environment, innovations in the hardware used in substations are necessary. Only new generation technologies that are small, efficient, heat-dissipating, or can optimize power-up sequences can fully tap into 5G's impressive transmission rates.
5G also faces a hurdle in that it has difficulty penetrating obstacles such as buildings and trees. Due to the limited coverage of high-frequency bands, severe interference can reduce data speeds. This also makes 5G unsuitable for rural areas, as implementing 5G is neither economical nor environmentally friendly. 5G is unlikely to cover sparsely populated areas, and some consumers may not be able to afford 5G-enabled terminals. Reduced availability makes it unrealistic for all terminals to adopt 5G.
Another point is the security issues that 5G may cause, because it connects so many devices together, and any link may cause security risks if it is attacked by a network. For example, a mobile phone connects to a video doorbell, which is connected to a smart lock, and the smart lock is connected to a security system; a network hacker may attack any of these devices and threaten all other devices due to their interoperability and connectivity.